The DSM-5 autism checklist can help you identify key behaviors and prepare for an evaluation. Here’s what you need to know:
- Focus Areas: The DSM-5 outlines two main areas for autism diagnosis:
- Social Communication Challenges: Issues like limited eye contact, difficulty with conversations, and struggles forming relationships.
- Repetitive Behaviors: Hand flapping, strict routines, intense interests, or unusual sensory responses.
- Parent Tracking: Observing and documenting your child’s behaviors at home, school, and social settings provides critical insights for healthcare providers.
- Tools to Help: Apps like Guiding Growth can simplify tracking, offering logs, reports, and organization tips to streamline the evaluation process.
- Next Steps: Use your observations to prepare for an autism evaluation, ask targeted questions, and plan interventions like IEPs or IFSPs based on your child’s needs.
This checklist empowers parents to take an active role in understanding their child’s development and supporting their unique needs.
Autism diagnosis criteria: explained (DSM-5)
Main DSM-5 Autism Criteria
The DSM-5 outlines two main areas for diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD): persistent difficulties in social communication and interaction and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities. These traits must appear during early development. Here’s a closer look at the key behaviors clinicians focus on.
Social Communication Signs
To meet the criteria, a child must show ongoing difficulties in all three of these areas:
- Social-Emotional Reciprocity
This includes challenges like limited back-and-forth conversations, trouble sharing interests or emotions, unusual ways of approaching others, or struggles with pretend play. - Nonverbal Communication
Signs may involve reduced eye contact, fewer facial expressions, difficulty using gestures, or trouble understanding body language. - Relationship Challenges
These can show up as difficulty adapting to social contexts, struggling to form friendships, limited interest in peers, or reduced participation in imaginative play.
Repetitive Behaviors and Patterns
For an autism diagnosis, a child must exhibit at least two of the following behavior patterns:
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Repetitive Movements | Hand flapping, finger flicking, lining up toys, echolalia, or walking on tiptoes. |
| Insistence on Sameness | Extreme distress over changes, rigid routines, specific greeting rituals, or fixed preferences for routes or food. |
| Restricted Interests | Intense focus on specific topics, strong attachment to unusual objects, deep knowledge in narrow areas, or fascination with object parts. |
| Sensory Differences | Extreme sensitivity to sounds or textures, unusual visual inspection, indifference to pain or temperature, or fascination with lights or movement. |
These behaviors must either be observed currently or documented in the child’s history. Clinicians also assess the severity of symptoms to determine the level of support required. It’s important to note that these challenges can shift over time, especially with intervention and support.
Parent Observation Guide
Keeping a detailed record of your child’s behaviors can be incredibly helpful during autism evaluations. This guide is designed to help you document key behaviors based on DSM-5 criteria.
Social Behavior Checklist
Here are some behaviors to track related to social communication:
| Behavior Category | What to Document | Recording Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Name Response | How quickly and consistently your child responds to their name, and whether the response is verbal or nonverbal | Note the time of day and the setting when observing |
| Eye Contact | How often and for how long your child makes eye contact, as well as the quality of their engagement | Observe during both structured activities and casual moments |
| Joint Attention | Instances where your child points to share interests, follows someone else’s pointing, or shows objects to others | Include both behaviors your child initiates and those they respond to |
| Social Play | Types of play, interaction with peers, and any imaginative play | Track preferred activities and any noticeable patterns in play |
Sensory and Routine Checklist
Use this section to document behaviors tied to repetitive actions and sensory sensitivities:
Movement Patterns
Pay attention to repetitive movements like hand flapping, rocking, or spinning. Note when these behaviors occur, their intensity, and whether they increase during moments of excitement or stress.
Routine Adherence
Track how your child reacts to:
- Changes in daily schedules
- Transitions between activities
- Adjustments to familiar routines
- New or unfamiliar environments
Sensory Responses
Observe and record your child’s reactions to:
- Different types and levels of sound
- Textures in food, clothing, or surfaces
- Light intensity or patterns
- Temperature changes
- Specific smells or tastes
Recording Methods
The Guiding Growth app can make tracking easier by offering tools like:
- Digital behavior logs with timestamps
- Features to identify patterns across various settings
- Customizable observation categories aligned with DSM-5 criteria
- Report generation to share with healthcare providers
When recording, include as much detail as possible, such as:
- Time and date
- Location and setting
- The activity taking place
- Duration of the behavior
- Any apparent triggers
- Interventions you tried (if applicable)
- The outcome
For a complete picture, consider combining digital logs with occasional video clips or behavior charts. These detailed records can help you stay organized and prepare thoughtful questions for discussions with professionals.
sbb-itb-d549f5b
Getting Ready for Evaluation
Preparing for an autism evaluation involves organizing your observations and documentation to ensure healthcare providers can make an accurate assessment based on DSM-5 criteria.
Organizing Your Records
Start by creating a detailed file that includes the following:
| Document Type | What to Include | Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Medical History | Developmental milestones, prior diagnoses, family history | Arrange chronologically with clear dates |
| Behavior Logs | Notes on social communication challenges and repetitive behaviors | Group observations by DSM-5 criteria |
| School Reports | Teacher feedback, academic performance, social interactions | Place the most recent reports at the top; highlight key behaviors |
| Video Documentation | Clips showing typical behaviors in various settings | Clearly label with dates and context |
To streamline the process:
- Organize records using DSM-5 categories, adding labels with dates, examples, and summaries for quick reference.
- Prepare a summary sheet that highlights your main observations and concerns.
If you’re looking for a tool to simplify this, consider using the Guiding Growth app. It can generate detailed reports based on the data you’ve tracked.
Questions for Evaluators
Once your records are ready, think about questions to ask during the evaluation. These can help clarify the process and next steps.
About the Evaluation Process
- What assessments will be used?
- How long will the evaluation take?
- Will it require multiple sessions?
- Which DSM-5 criteria will the evaluation focus on?
About Results and Next Steps
- When can we expect the results?
- How are severity levels determined?
- What interventions might be recommended based on the findings?
- How should we prepare for follow-up appointments?
Keep a notebook handy for these questions and any others that might come up. Bring copies of your documentation to the appointment, and check with the provider beforehand to see if they’d prefer to review your records in advance. Many evaluators appreciate having this information ahead of time as it helps them prepare for the session.
After the Diagnosis
Reading Your Report
Your child’s diagnostic report is an essential tool for planning the next steps. It outlines the severity of support needed, categorized into three levels:
| Severity Level | Social Communication | Restricted/Repetitive Behaviors |
|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Needs support; noticeable difficulty initiating social interactions | Inflexibility that may disrupt daily routines |
| Level 2 | Needs substantial support; significant challenges with verbal and nonverbal communication | Repetitive behaviors that are obvious and disrupt daily life |
| Level 3 | Needs very substantial support; severe difficulties with social interaction | Behaviors that greatly interfere with all areas of daily functioning |
Pay close attention to:
- Observations of specific behaviors
- Assessment results and scores
- Recommended interventions
- Support requirements for home and school settings
These details will help you tailor educational and developmental plans effectively.
IEP and IFSP Planning
Your child’s age determines the type of plan they’ll need:
- IFSP (Individualized Family Service Plan): For children under 3 years old, this plan emphasizes early intervention and family-oriented support.
- IEP (Individualized Education Program): For children aged 3 and older, this plan focuses on educational needs, accommodations, and goals.
To prepare for your meeting:
- Write down your child’s strengths and areas where they face challenges.
- Prepare questions about the available services and supports.
- Familiarize yourself with your rights under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA).
During the meeting, share observations from home, ask for regular progress updates, and actively participate in shaping the plan.
Using Guiding Growth
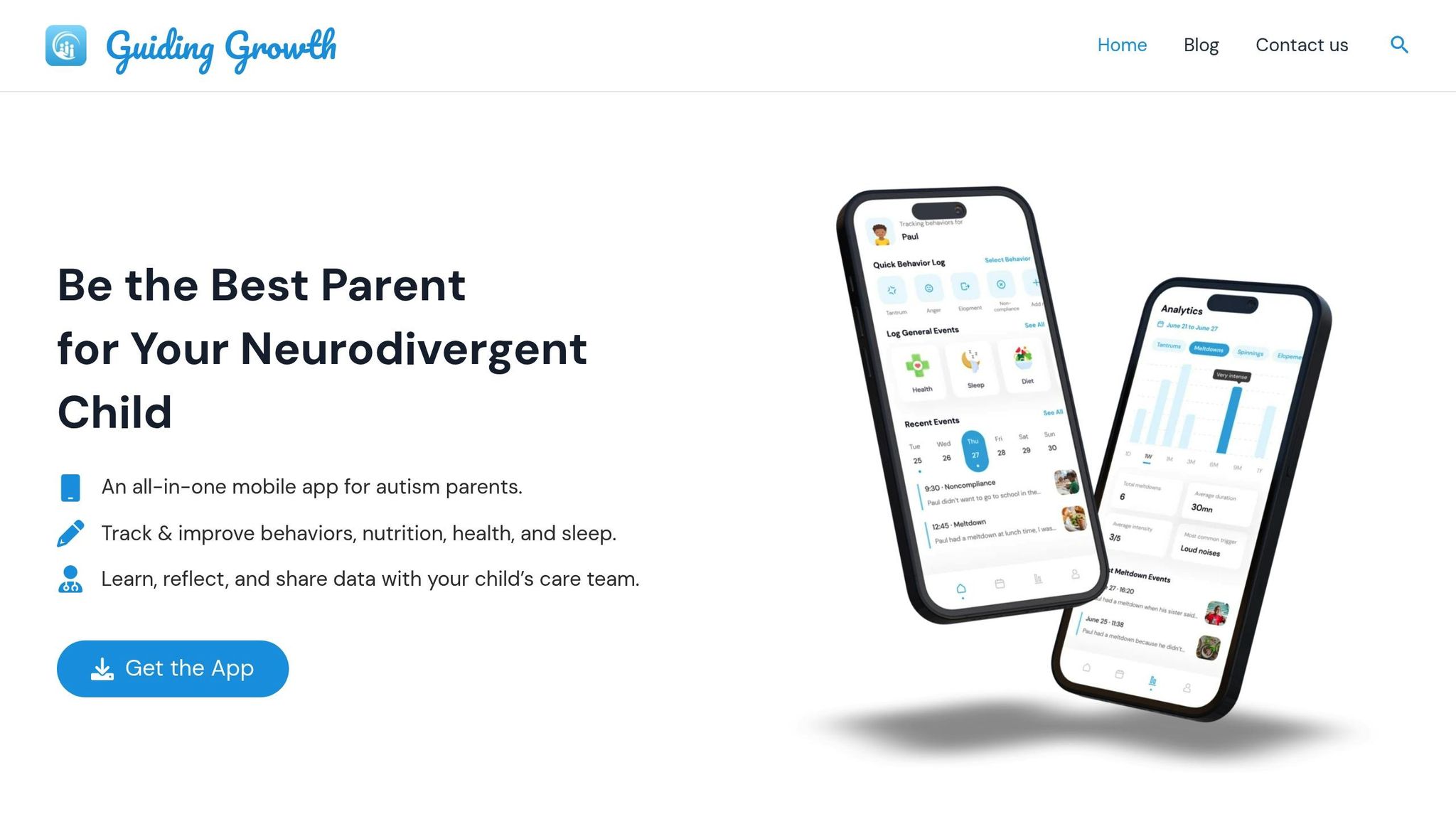
The Guiding Growth app can be a helpful tool to manage and monitor your child’s progress. It allows you to:
- Track behaviors and responses to interventions.
- Create progress reports for healthcare providers.
- Log sleep patterns, diet, and daily activities.
- Stay connected with your support team through clear communication.
These features make it easier to stay organized and ensure your child’s needs are being met.
Summary
The DSM-5 autism checklist serves as a helpful resource for parents navigating the evaluation process. By observing behaviors across different settings, consistent patterns can emerge. Structured observation methods allow for a clearer understanding of social communication challenges and repetitive behaviors, enabling professionals to make accurate and timely diagnoses [1].
Here are a few tips to get the most out of the checklist:
- Document specific examples of behaviors in various environments.
- Pay attention to frequency and intensity when recording patterns.
- Monitor changes over time to spot trends or new developments.
- Share well-organized notes with healthcare providers for better insights.
For added support, the Guiding Growth app can help by logging observations and creating detailed reports, making treatment planning more informed and effective.
FAQs
How can I use the DSM-5 autism checklist to prepare for my child’s evaluation?
The DSM-5 autism checklist serves as a practical guide for parents aiming to understand behaviors and traits that might suggest autism. To make the most of it, begin by carefully reviewing the checklist and observing how your child behaves in everyday situations. Pay attention to any recurring patterns, challenges, or strengths that match the criteria outlined in the DSM-5.
It’s helpful to document specific examples of your child’s behaviors. For instance, note how they communicate, engage socially, or react to sensory experiences. Keeping a detailed record over time can provide valuable context for healthcare providers, helping them better understand your child’s unique needs.
For a more organized approach to tracking and analyzing these behaviors, tools like Guiding Growth can be a useful resource. They allow you to structure your observations and create detailed insights to share with your child’s evaluation team.
How can I effectively track and document my child’s behaviors using DSM-5 criteria?
Tracking your child’s behaviors through the lens of DSM-5 criteria can provide valuable insights into their needs and daily patterns. One effective approach is to keep a record of key areas like meltdowns, stimming behaviors, sleep habits, and eating routines. Over time, this process can help you identify triggers and recurring patterns that might affect their overall well-being.
To make this easier, consider using autism-focused parenting tools, such as apps designed for detailed behavior tracking. These tools not only help you stay organized but can also generate useful insights and create reports. Such reports can be incredibly helpful when sharing information with caregivers or healthcare providers, aiding in evaluations and ongoing care.
How can Guiding Growth help me track and understand my child’s autism-related behaviors and progress?
Guiding Growth offers parents a simple and effective way to monitor and understand important aspects of their child’s daily life – like behaviors, sleep habits, diet, and activities. By organizing this data, the app helps uncover patterns and provides insights into factors that may be shaping your child’s development.
It also streamlines collaboration with healthcare providers, caregivers, and family members by creating clear, data-based reports. These reports empower you to make well-informed decisions and advocate for your child’s needs, giving you greater confidence and support throughout your parenting journey.


