Tracking food is a powerful way to improve autism-related diets. It helps identify sensory preferences, prevent nutrient gaps, and link foods to behavioral changes. Using the right tools, like apps with behavior tracking and nutrient analysis, can make this process easier and more effective.
Key Takeaways:
- Why Track Food? Manage sensory sensitivities, improve nutrition, and identify triggers for mood or behavior changes.
- Common Challenges: Sensory issues (e.g., texture preferences), nutrient deficiencies (e.g., low zinc), and gut health problems (e.g., constipation).
- Features to Look for in Apps: Sensory logging, behavior tracking, secure data storage, and nutrient analysis.
- How to Use Data: Spot patterns, plan meals around preferences, and share insights with healthcare providers.
Tracking consistently can lead to better meal acceptance, fewer meltdowns, and improved sleep. Tools like Guiding Growth simplify the process by combining food and behavior data in one place. Start small, log daily, and use the insights to customize your child’s diet for better health and well-being.
Common Food and Diet Challenges in Autism
Food Textures and Sensory Issues
Around 70% of autistic children show unusual eating habits [1], often tied to sensory sensitivities. Texture preferences can be particularly strong – some children may accept smooth foods like yogurt but completely avoid crunchy vegetables, leading to nutrient gaps.
| Texture Type | Common Challenges | Impact on Nutrition |
|---|---|---|
| Crunchy | Avoidance of raw vegetables | Lower fiber intake |
| Smooth | Preference for pureed foods | Limited food variety |
| Mixed | Struggle with foods having multiple textures | Difficulty achieving balanced meals |
Tracking these patterns can help identify problem areas and guide meal adjustments, as seen in later strategies for meal planning.
Key Nutrient Gaps in Autism
Nutritional deficiencies are a recurring issue for autistic children. For instance, 45% of them have low zinc levels, which are essential for immune function. Selective eating habits, seen in 50-80% of cases, are a major contributor to these gaps, affecting brain health and gut function. Using tracking apps to log meals and compare them to nutritional standards can help pinpoint these deficiencies.
How Digestion Affects Behavior
The connection between gut health and behavior is especially pronounced in autism. About 70% of autistic children deal with chronic constipation [2], which can lead to noticeable behavioral changes:
| Digestive Issue | Behavioral Impact | Time Frame |
|---|---|---|
| Constipation | Irritability and self-injury | Within 24 hours |
| Food sensitivities | Anxiety and aggression | 6-24 hours |
| GI discomfort | Sleep issues and social withdrawal | During discomfort |
Research shows that 78% of autistic children with gastrointestinal problems exhibit more intense repetitive behaviors. This underscores the importance of food tracking to identify triggers within specific time frames. Effective tracking tools should log both meals and related behaviors, a feature we’ll explore further when reviewing tools.
Selecting Food Tracking Apps for Autism
Must-Have App Features
To effectively track the link between digestion and behavior, it’s essential to use tools that record both nutritional and behavioral data at the same time. Security is a critical factor.
Using Guiding Growth for Diet Tracking
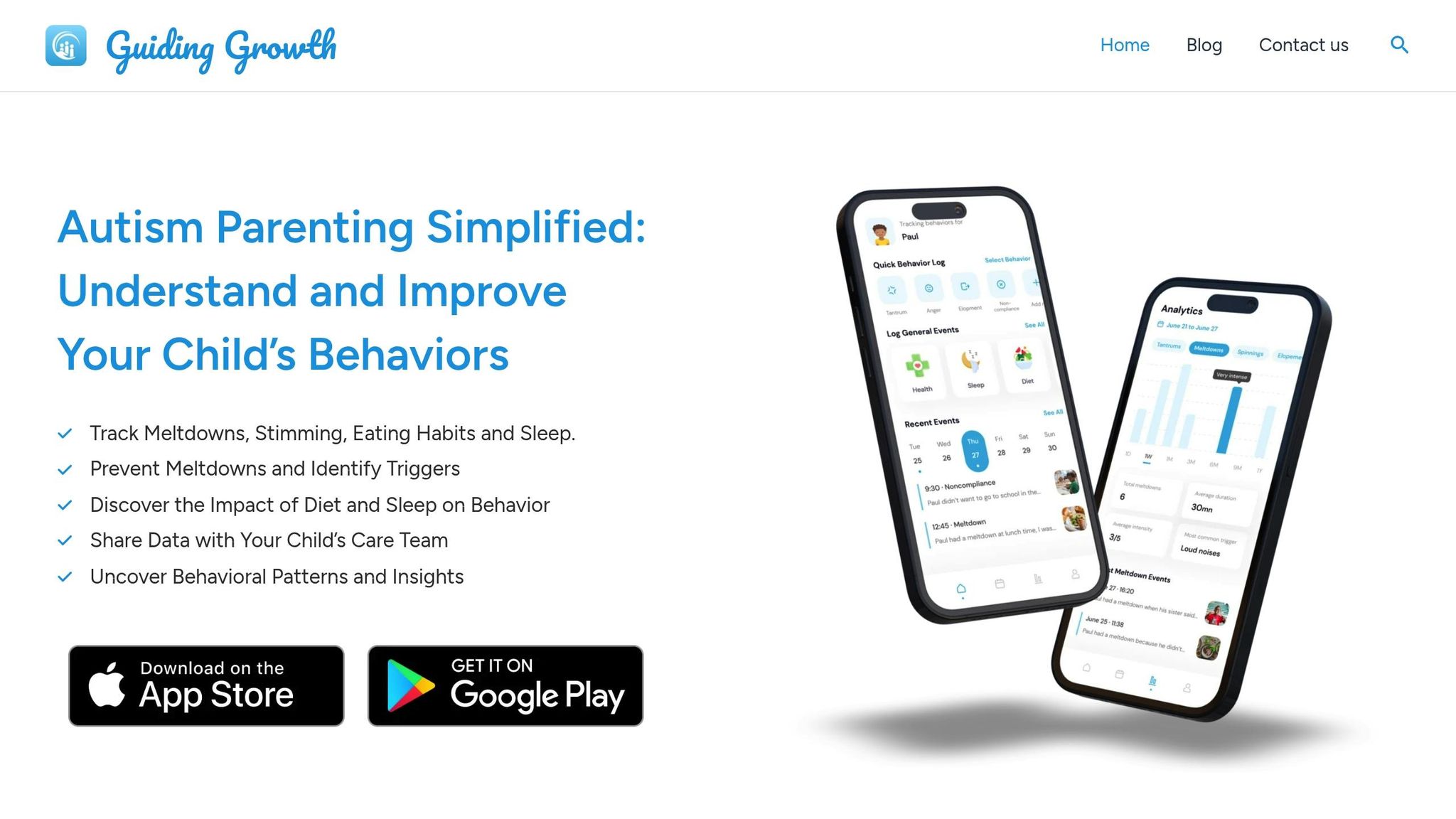
Guiding Growth is a standout option for linking dietary data with other key aspects of autism care. Its approach aligns with the digestion-behavior patterns mentioned earlier, making it easier to pinpoint triggers.
With this app, parents can:
- Log meals alongside related behaviors
- Spot connections between food and behavior patterns
- Create combined dietary and behavioral reports
Guiding Growth uses AI generated smart reports to uncover subtle patterns, making it a practical tool for tracking foods and related metrics in one place.
sbb-itb-d549f5b
Adding Food Tracking to Your Daily Schedule
Incorporating food tracking into your daily autism care routine can help you identify links between diet and behavior. With a little planning and the right strategies, you can make this process manageable and insightful.
Tracking Foods Based on Sensory Needs
When tracking food choices, focus on sensory factors that influence your child’s eating habits. Use a structured method to log these preferences, aligning them with the sensory logging features in your app:
| Sensory Aspect | What to Track | Example Rating Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Hot, warm, room temp, cold | Preferred/Neutral/Avoided |
| Flavor Intensity | Mild to strong | Color coding (e.g., green = accepted, red = refused) |
| Visual Appeal | Size, color, presentation | Simple/Mixed/Complex |
To make this part of your routine, log meals during natural transitions, like after breakfast. This keeps the process stress-free and easy to maintain.
Using Tracking Data for Meal Plans
Once you’ve gathered enough data, use it to create meal plans tailored to your child’s preferences. Patterns in the logs can guide you in crafting meals that are more likely to be accepted. For instance, families who consistently tracked meals reported a 40% improvement in meal acceptance rates, according to a study on autism feeding programs [3].
Here are three key areas to focus on when planning meals:
- Peak Eating Times: Identify when your child is naturally hungriest and schedule main meals during those times.
- Environmental Factors: Note the settings that encourage better eating, such as specific plates or favorite seating arrangements, and replicate those conditions.
- Food Combinations: Track which pairings work well. For example, if serving a new food alongside a favorite increases acceptance, include this strategy in future meals.
Making Decisions with Food Tracking Data
Once you’ve developed consistent tracking habits (as explained in Adding Food Tracking to Your Daily Schedule), the next step is to analyze your data effectively. Here’s how you can make sense of it:
Finding Food and Behavior Links
To understand how food choices impact your child’s behavior, you’ll need to systematically review your tracking data. Pay attention to these areas:
| Observation Type | What to Track | Time Window |
|---|---|---|
| Immediate Reactions | Mood changes, energy levels | Within 1-2 hours |
| Digestive Response | GI symptoms, comfort level | 24-48 hours |
| Sleep Patterns | Quality, duration | Same day and following night |
Look for recurring patterns, such as certain foods consistently influencing your energy or mood. Use your tracking app’s timeline features to identify delayed reactions. To pinpoint triggers, make it a habit to log symptoms alongside meals for at least 2-4 weeks.
Sharing Data with Health Providers
When preparing for appointments, transform your tracking data into clear, concise reports. Focus on these elements:
- Key Patterns: Highlight recurring reactions to particular foods or food groups.
- Effective Strategies: Note what has worked to improve your eating habits or well-being.
"When analyzing food tracking data, it’s important to consider factors beyond just the food itself, such as meal timing, portion sizes, and environmental factors during meals" [4].
These insights complement the meal planning techniques discussed earlier, creating a cycle of observation and adjustment.
To make the most out of your discussions with healthcare providers:
- Use visualizations to show food acceptance trends.
- Emphasize any significant changes you’ve noticed.
- Come prepared with specific questions to guide the conversation.
Solving Common Food Tracking Problems
Once you’ve pinpointed dietary triggers through data analysis, the next step is tackling common challenges in food tracking with practical solutions.
Managing Food Refusal
Food refusal is a challenge faced by up to 72% of children with autism. To address this, keep a detailed log of both accepted and refused foods. Use your app’s tools to connect refusal incidents with mood and environmental factors, giving you a clearer picture of patterns.
Try food chaining techniques – this means gradually introducing foods with similar textures or flavors to those your child already accepts. By documenting these efforts in your app, alongside related behaviors and settings, you can track progress over time and make adjustments as needed.
Simplifying Daily Tracking
Keeping food tracking simple is key for staying consistent. Here are some ways to make it easier:
- Take photos of meals to log them later.
- Set up shortcut codes for meals you frequently prepare.
- Incorporate logging into your daily routines.
For parents with packed schedules, batch-prepping meals can save time. Plan and prepare meals for the week, photograph them, and use these images as references for your logs. This method reduces the day-to-day tracking effort while keeping things consistent.
Conclusion: Better Diet Management Through Tracking
Tracking food intake allows 91% of parents to pinpoint behavioral triggers. Tools such as Guiding Growth help connect diet patterns with symptoms, complementing the meal planning strategies covered earlier.
Using these tracking methods alongside the data-sharing techniques mentioned earlier enables parents to tackle common dietary challenges associated with autism. The step-by-step approach outlined here helps parents log meals to identify triggers, gradually introduce new foods, and address sensory sensitivities.
Smart tracking tools are transforming how parents manage autism-related dietary issues by turning logged data into actionable changes. By applying the strategies in this guide, parents can strengthen their child’s nutritional health and overall well-being.


